Coaxial cable
Internet on cable TV
2.2.3 Coaxial cable

Still copper.
Again, change voltage
to get analog signal.
Frequency
= rate of change of voltage.
Compared to twisted pair phone line:
Longer distances. Low noise.
Higher speeds (historically, though advanced DSL may challenge this).
Used to be used in telephone backbone.
Now replaced by fiber optic.
Main surviving installed base of coax is cable TV.
Main surviving installed base of coax is cable TV local loop.
Internet can be provided over this too.
Like telephone network, cable TV network backbone has gone fiber and wireless.
Local loop coax.
2.7.2 Shared local loop
Unlike telephone, local loops are
shared among multiple houses.
Sharing is no problem for broadcasting.
For Internet, though, sharing means:
- Contention
problems.
- Privacy/security problems.
As Internet access taken up,
the cable companies have been progressively reducing sharing
to smaller numbers of houses per cable
(still shared, but not as much contention).
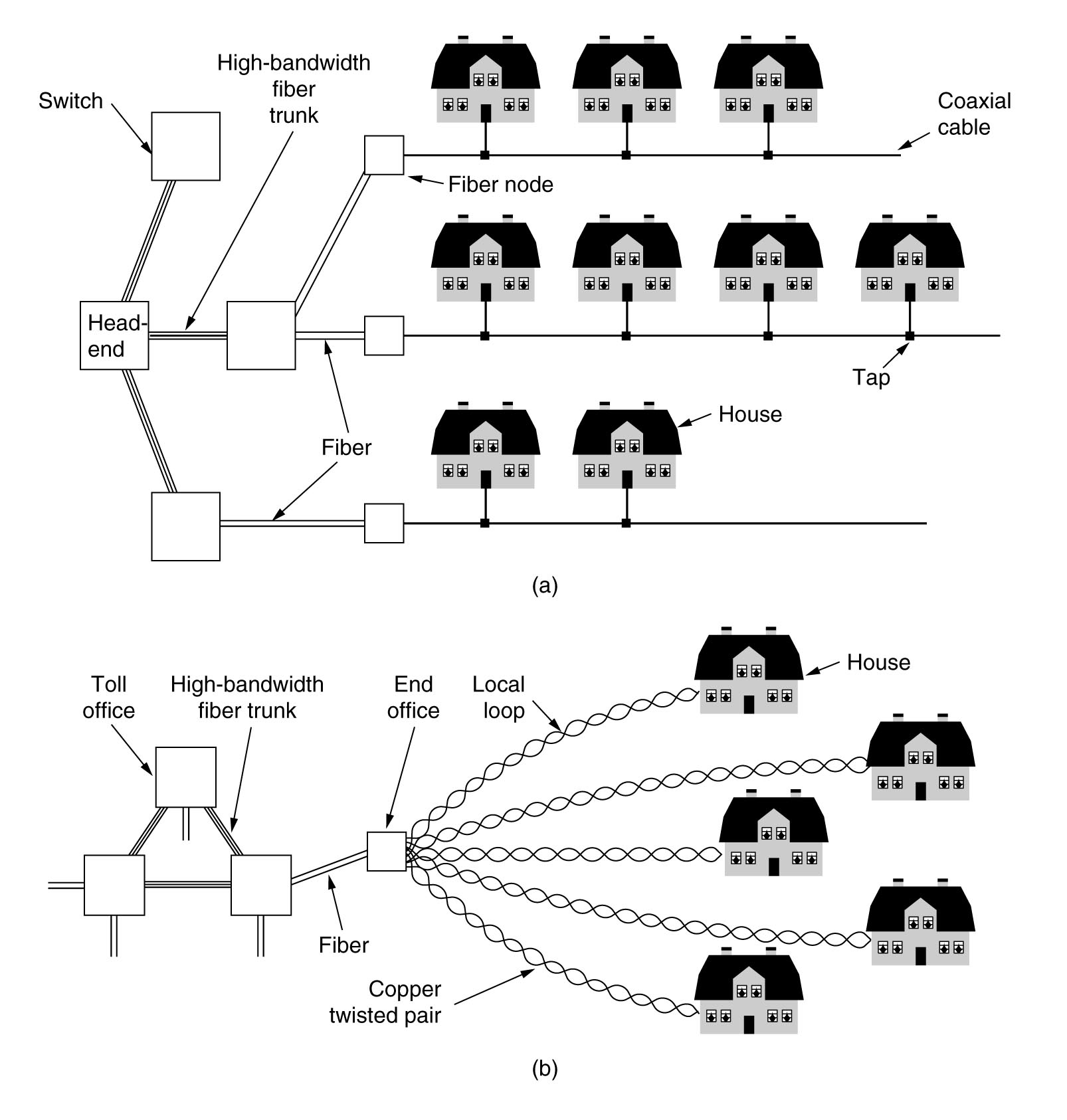
The difference between:
(a) the (shared, designed for 1-way broadcast) cable TV local loop
and:
(b) the (non-shared, designed for 2-way comms) telephone local loop.
Telephone network would be simply better for Internet
if it were not for the fact that
coax is faster than phone line.
2.7.3 Spectrum Allocation
TV and Internet coexist on same cable,
using different frequency bands.
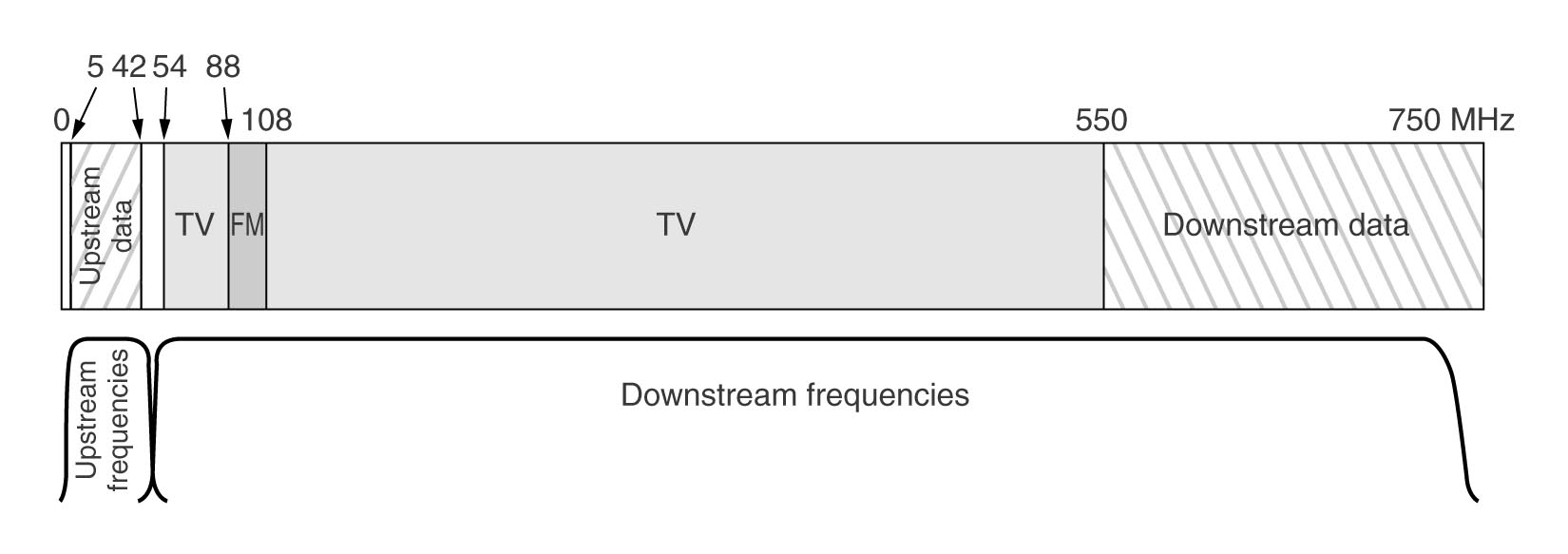
Note that TV is all downstream.
Can use upstream amplifiers that work only below 42 MHz,
and downstream amplifiers that work only above 54 MHz.
2.7.4 Cable modems
With coax, still need analog modulation to send digital data.
QAM-64 or higher used downstream.
Upstream not as good a line.
Simpler scheme like
QPSK needed to get through.
Contention is on upstream (multiple senders).
Aloha / Ethernet-like
system: If contention, back off, wait random time, try to send again.
No contention on downstream - only one sender, the broadcaster.
Everyone can see all traffic. Only note what is addressed to you.
For privacy, need encryption.

2.7.5 DSL v. Cable
- Cable faster than DSL?
Hard to say.
- Cable bandwidth is shared among multiple users.
Speed quoted may not be achieved.
Depends on contention.
- Cable speed more unpredictable than DSL
as neighbours log on and off.
- It's for home only.
Few businesses have cable (they didn't sign up for cable TV).
- Telephone network more reliable (under power outages etc.)
than cable TV network.
Built that way, since so much more important.
- Cable has worries about privacy/encryption
that DSL doesn't have.



