Wireless
2.3 Wireless
Fiber optic may eventually dominate the cable world,
but it will never dominate
all comms.
The future is fiber optic and wireless.
Uses of wireless:
- laptops, notebooks, palmtops, PDAs, mobile phones
- on aircraft, in cars, at sea
- in airports,
cafes, at conferences
- on the beach,
in mountains, fields, remote areas
- Work
- Mobile workers - taxis, fleets, trucks, ships, aircraft
- Military -
bring your own network with you
- don't rely on local one.
- Mobile-specific services
- GPS phones
(and here)
- iPhone applications
- All iPhone applications
- see Navigation
- Where is nearest shop to where I am now?
- Show me local street map.
- Whrrl,
Google Latitude
- Show me where all my friends are as dots on a map
- find friends in streets nearby.
- Clothing with barcodes
that can be read by any camera
(don't need scanner).
Point smartphone at them and barcode identifies them
and can send you to their webpage on your smartphone.
- All this could lead to a return in urban areas
to a "village" environment
- where you can easily find people,
and you know who and where everyone is.
- (Local area) alternative to cables
- Personal area network - connecting
PC keyboard, peripherals (as alternative to cables)
- Wireless home network -
feed broadband Internet access to
multiple PCs and laptops,
which may be moved from room to room
- wiring a building where installing cable is difficult (e.g. old building,
remote building)
- Similarly, fixed location where installing line is too much overhead.
e.g. Vending machine uses wireless to call home with its stock levels.
Giving it its own phone line for 1 call a day is too expensive
(install, monthly charge).
- Wireless home network -
link small devices - fridge, TV, phone,
burglar alarm, smoke alarm, security cam.
e.g.
Belkin WeMo.
- wearable computing
- (Wide area) alternative to cables
- alternative to laying long- (or even short-) distance cable
(no right-of-way is needed, e.g. in crowded urban region)
- long-distance satellite links (as alternative to laying ocean cable)
- VSAT's
(also here)
- very small satellite:
- receivers
(1-way broadcast satellite TV,
GPS)
-
and transmitters
(satellite phones for remote areas,
third world countries with poor telecom networks)
- Broadcasting of data
in general - Satellite makes more sense than fiber.

Fixed wireless v. Mobile wireless
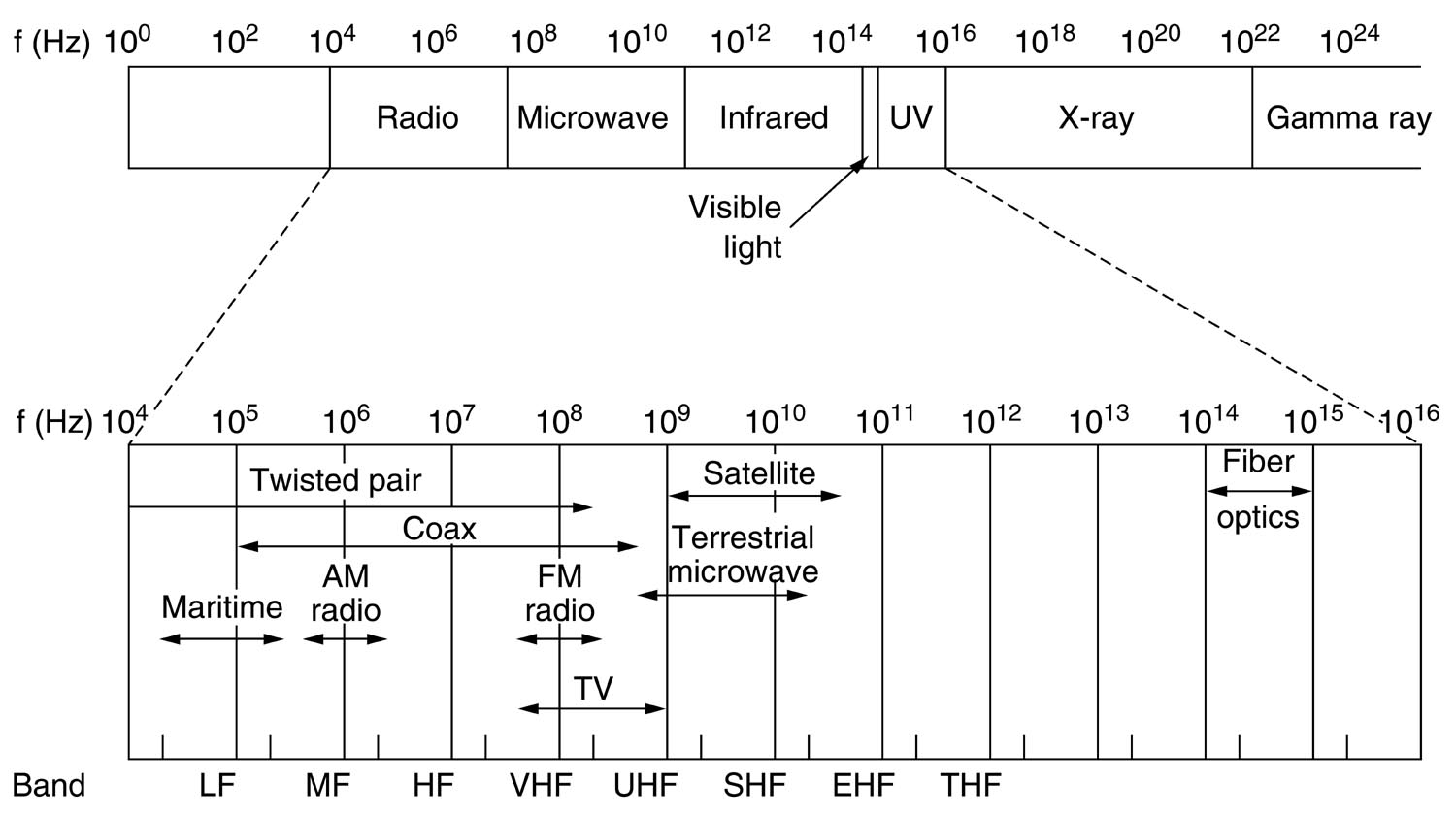
Summary of electromagnetic spectrum.
To the left: long wave, low f.
To the right: short wave, high f.
Useful f's for data
Can use these to send data, in order of increasing frequency:
- radio - lower f - lower bandwidth
- microwave
- infrared
- visible light (fiber optics) - higher f - higher bandwidth
Higher f than visible light are dangerous to humans. Not used.
High f absorbed or blocked by objects
- radio - low f, passes through walls etc.
- microwave - ok at low f - at high f is absorbed by water (rain)
- infrared - higher f, can't pass through walls
- visible light - even higher f -
obviously can't pass through walls
So in practice:
- radio - lower bandwidth
- microwave - the most useful
- mobile phones
- wireless local loop (fixed wireless)
- satellites - TV, telephone backbone, Internet backbone
- on land, long-distance telephone links
(most long-distance links before fiber optics),
- at high f is absorbed by water (rain) - have to route around / correct errors
- infrared - can't pass through walls
- remote controls, car keys
- connecting peripherals, e.g. cordless mouse
- light - can't just send through air - have to send in fibers
Why is wireless different?
Lots of issues, such as:
- Mobile phone pickup when switched on
- Mobile phone handoff
- Increased delay times (e.g. satellite round trips)
- Satellite handoff
- Satellite 2 Satellite routing of packets
- Increased errors (interference, weather)
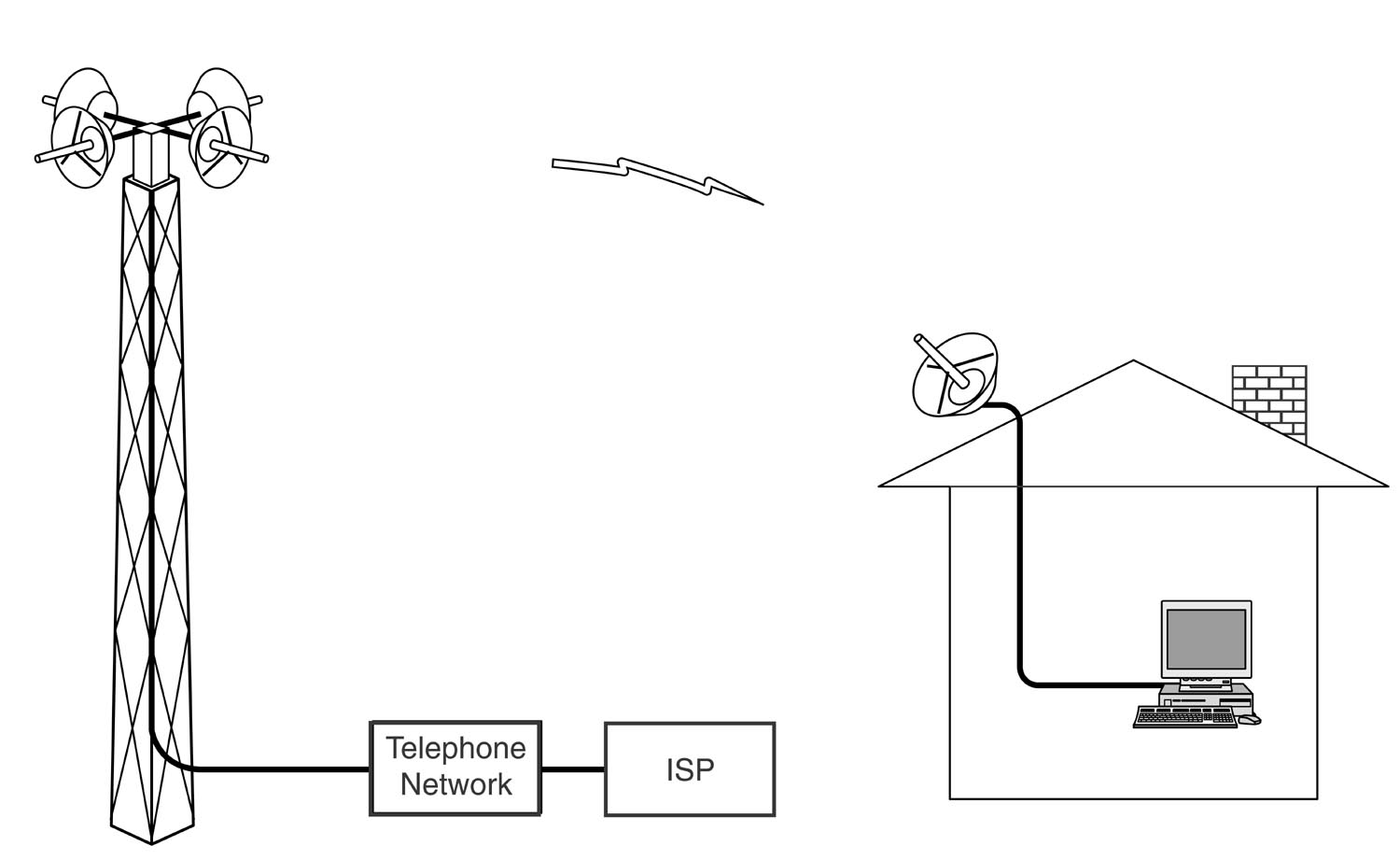
2.5.3 Fixed wireless
Wireless local loop.
Way to break telephone company monopoly of local loops.
Fixed wireless - e.g. in the home.
User doesn't move. No problems like mobile phone handoff.
High f microwaves.
Bandwidth massive (36 Gbps) but shared among many
(thousands of) users of one tower.
See "contention ratio".
- IEEE 802.16 Working Group
- Large amount of errors:
- Fixed-wireless broadband in Ireland:
-
Irish wireless broadband permits awarded
- e.g.
Irish Broadband
wireless broadband ISP.
"Irish Broadband is rolling out a ..
wireless broadband network
across the Dublin area.
"High sites" form the building blocks of the network.
Each high site comprises a tall building or mast equipped with a broadcast transmitter.
Customers connect to the network using a small antenna on their roof.
This antenna must be within line of sight of an Irish Broadband site."
Unlike mobile phone signals, the signals cannot penetrate walls.
- See
Irish broadband speeds.
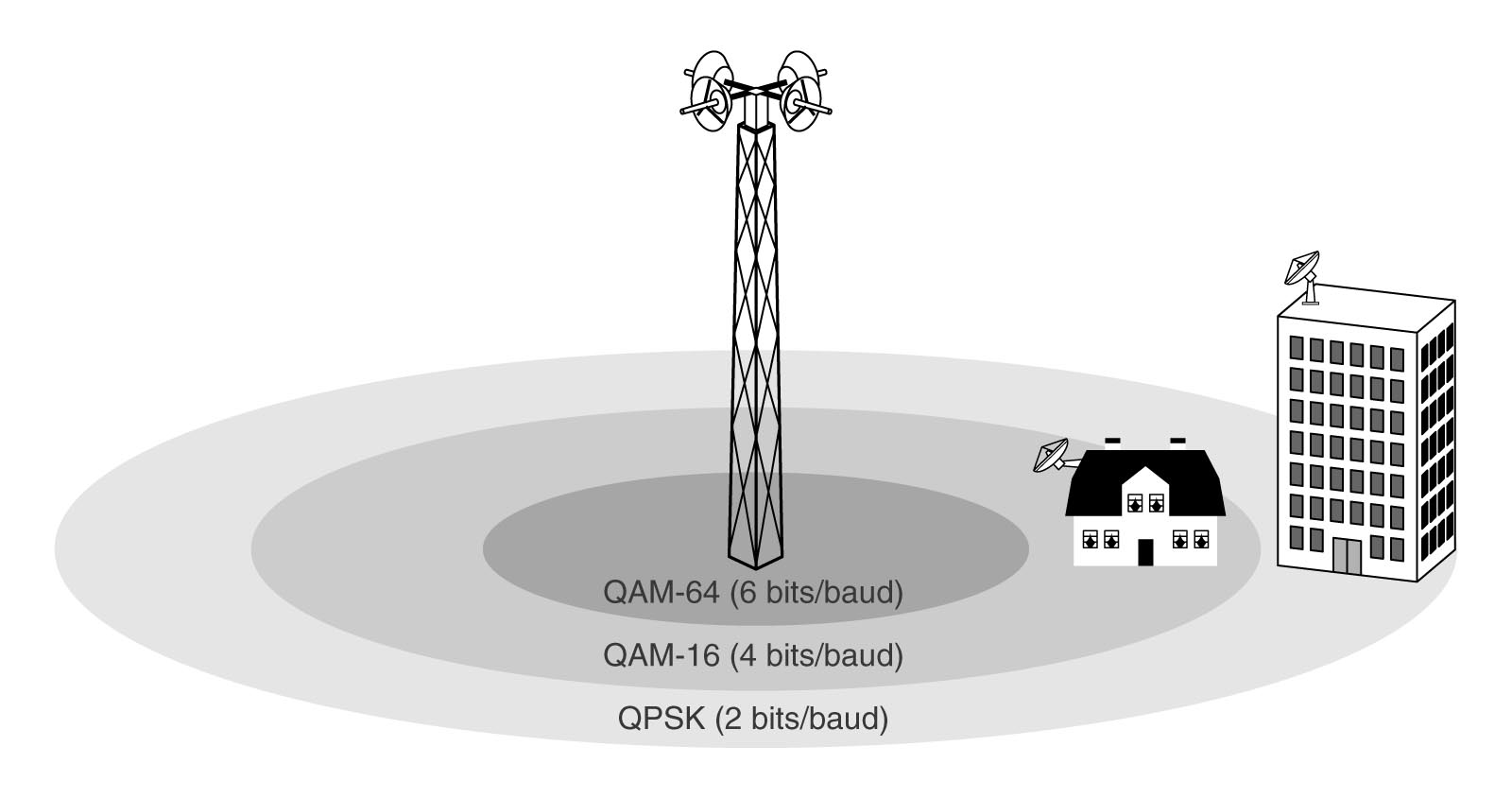
Reduced bandwidth the further you get from the base station.
WiMax - 802.16 goes mobile
- "WiMax" (implementations of 802.16)
- Fixed WiMax - "last mile" - dish on roof
- Mobile WiMax - alternative to using mobile phone network
- mobile phone network itself may use WiMax
People mobile, coming to fixed LAN locations.
Connect to local LAN
(e.g. in cafe, at conference, in library)
rather than connect
direct to phone network as in mobile phones.
Strong competitor of mobile phone network (for data comms at least),
but wireless LAN "hotspots"
may not exist where you want.
Semi-mobile user, going from base to base.
Competitor also of Ethernet cable LAN
- much easier to install.
Wireless home network -
feed broadband Internet access to
multiple PCs and laptops,
which may be moved from room to room
Short-range.
Cordless mouse, keyboard, headphones, etc.
PDA file synch.
Wireless hands-free mobile phone headset.




